Graduation Rates
Graduation and retention rates of undergraduates in Minnesota's postsecondary institutions
Graduation is a goal of most new-entering full-time students entering Minnesota colleges and universities; however, not all of them complete their studies at the same institution as they entered. While some students will leave to transfer and complete somewhere else, others will drop out of college altogether.
The graduation rates shown track graduation rates of first-time, full-time students who entered a four-year institution six years prior to entry and completed a bachelor’s degree at that same institution. At Minnesota’s State Colleges (public two-year) graduates are tracked three years prior to entry. The State College’s transfer-out rate is also included since many of those institutions serve students who intend to transfer before receiving a credential. Transferring is seen as a successful outcome of the mission of State Colleges.
Learn More- Graduation Rate Trends of Minnesota Institutions
- College Navigator has more institution specific graduation rate information
Retention Rates
There are two data sources of retention data available.- The U.S. Department of Education tracks the retention of first-time full or part-time undergraduates from fall enrollment in their first year to fall of their second year. Retention rates are not reported by race/ethnicity.
- Data from Minnesota's Statewide Longitudinal Education Data System tracks Minnesota high school graduating classes enrolled in any Minnesota institution from first year to second year. These data enable reporting by race/ethnicity and enable reporting of retention at any institution not just the first institution attended.
First to Second Year Retention in a Minnesota Postsecondary Institution by Race/Ethnicity, 2006 to 2015
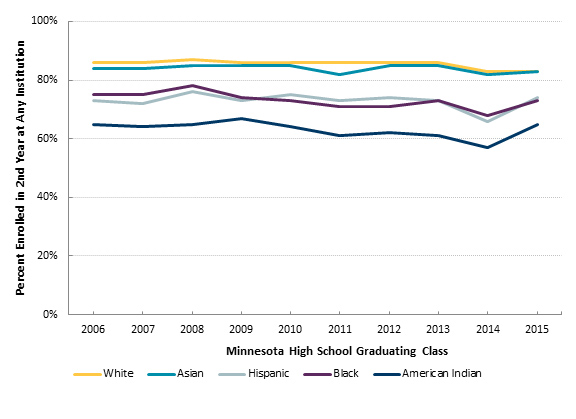
Source: Statewide Longitudinal Education Data System
About Graduation Rates
The graduation rates reported here were developed by the U.S. Department of Education's National Center for Education Statistics, to be used for the Integrated Postsecondary Education Data System (IPEDS), Graduation Rate Survey. These national standardized rates were devised so graduation rates could be compared across institutions.
The graduation rate tracks a cohort of students (defined as new-entering, full-time, first-time, degree-seeking) from their time of initial enrollment in an institution until they complete their program within 100%, 150% or 200% of normal time to program completion at the same institution. The standard reported rate is 150% of normal time. For a bachelor's degree program students graduating within six years are successful completers, while associate degree or certificates below bachelor's degrees completed within three years are successful completers.
Graduation rates measure whether students are completing their studies and institutional effectiveness in facilitating student completion. High graduation rates may indicate appropriately targeted student recruitment, effective campus communication and scheduling, strong instruction and advising, and accessible student support services. Other variables, such as the academic preparation of students, collegesadmissions selectivity, student demographics and financial support, also influence graduation rates.
Undergraduates who transfer into an institution are not included in the cohort used to calculate an institutions graduation rate. Likewise, undergraduates who transfer out of an institution adversely affect an institution's graduation rate.
According to data from the National Student Clearinghouse, Minnesota ranks high in the percent of undergraduates starting at Minnesota institutions who graduate from another institution than the one started. Percent graduating from another institution is 24 percent of public four year, 18 percent of public two year and 12 percent of private four-year starters.
Related LinksQuick Links
- Why College?
- Explore Your Interests & Careers
- Prepare at School
- Summer Academic Enrichment Program
- Earn College Credit in High School
- Recommended High School Classes & Graduation Requirements
- Advice for Students with Disabilities
- Succeed as an Adult Student
- Useful College Prep Resources
- Minnesota Goes to College!
- Get Ready Program Overview
- College Planning Presentation Information
- College Navigator Presentation Request Form
- Minnesota Indian Scholarship Program Outreach
- Competitive Grant Programs
- Dual Training Grant
- Public Engagement Calls
- "Life After Now" Podcast
- Certified Nursing Assistant Training
- Direct Admissions Minnesota
- Collecting Data from Minnesota Postsecondary Institutions
- Campus Financial Aid Administrator Resources
- Statewide Financial Aid Conference
- Campus Student Enrollment Reporting Resources
- Ordering Materials for Your Students
- Supplementing Your College Counseling
- Early Awareness Efforts
- Student Homelessness in Higher Education Resources
- Shared Library Resources
- MN FAFSA Tracker
- Campus Sexual Violence Prevention and Response
- Statewide FAFSA Filing Goal
- Financial Aid Estimator
- Online Applications
- About Financial Aid
- What Does College Cost?
- Tips for Lowering the Cost of Higher Education
- Institutional Payments
- Financial Aid You Don't Repay
- Financial Aid You Must Repay (Student Loans)
- Financial Aid You Earn
- Military Service Education Benefits
- Reduced Out-of-State Tuition Options
- Education Tax Benefits
- New Video Demystifies Paying for College
- Public Service Loan Forgiveness
- Useful Online Resources
- Ready, Set, FAFSA!
- Data Maps and Infographics
- Educational Attainment Goal 2025
- Minnesota Measures
- Minnesota P-20 Statewide Longitudinal Education Data System
- College Readiness & Participation Data
- Student Enrollment Data
- Degrees, Graduation Rates, Attainment & Outcomes
- Financial Aid Data & Trends
- Tuition & Fees Data
- Student Health and Safety
- Institution and Data Search
- Transfer Students
- Research Reports
- A-Z Data Table Index




